Hypertonic solutions
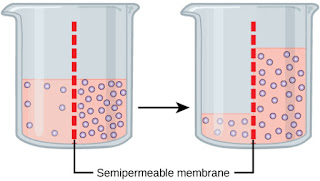
Hypertonic solutions are solutions where the water potential of the solution outside the cell is lower than the water potential of the solution inside the cell. There is a concentration gradient (difference in concentration) which causes water to move from an area of high water potential, which is in the cell, to an area of high water potential, which is outside the cell, down a concentration gradient.
The net movement of water out of the cell could result in 2 things happening, depending on the type of cell from which water were moving out from. If water moves out of an animal cell, the cell shrivels and shrinks (animal cell shrinking due to water movement out of the cell is called crenation).
If this took place in a plant cell, the plant cell would not shrink but the cell membrane and the cytoplasm move away from the cell wall; this process of moving away from the cell wall is called plasmolysis. It causes the cell to be flaccid (limp) and the plant cell to wilt.
Hypotonic solutions
Hypotonic solutions are solutions where the water potential (concentration) of the solution inside the cell is lower than the water potential outside the cell. Because water moves from an area of high water potential to an area of low water potential, down a concentration gradient, water moves into the cell from an area of high water potential outside the cell to an area of low water potential inside the cell. The net (overall) movement is into the cell.
In animal cells, the large movement of water into the cell causes the cell to swell up and burst (lysis). In plant cells, the movement of water into plant cells causes the plant cell to swell up (become turgid) and the cell membrane and cytoplasm to push against the cell wall. The plant cell does not burst because the rigid cell wall surrounds the cell, resisting pressure and preventing the cell from bursting.
Think of ‘hypo’ and ‘low’ to remember it if you’re confuse d between hypotonic and hypertonic solutions. Hypotonic solutions have a lower water potential.
Isotonic solutions
Isotonic solutions are solutions where the water potential of the solution inside the cell is the same as the water potential outside the cell. Because the water potential inside and outside of the cell is the same, there is no change in the concentration gradient meaning there is there is no net (overall) movement of particles either into or out of a cell. Water diffuses into and out of the cell by osmosis but there is still no net (overall) movement of particles into and out of the cell.